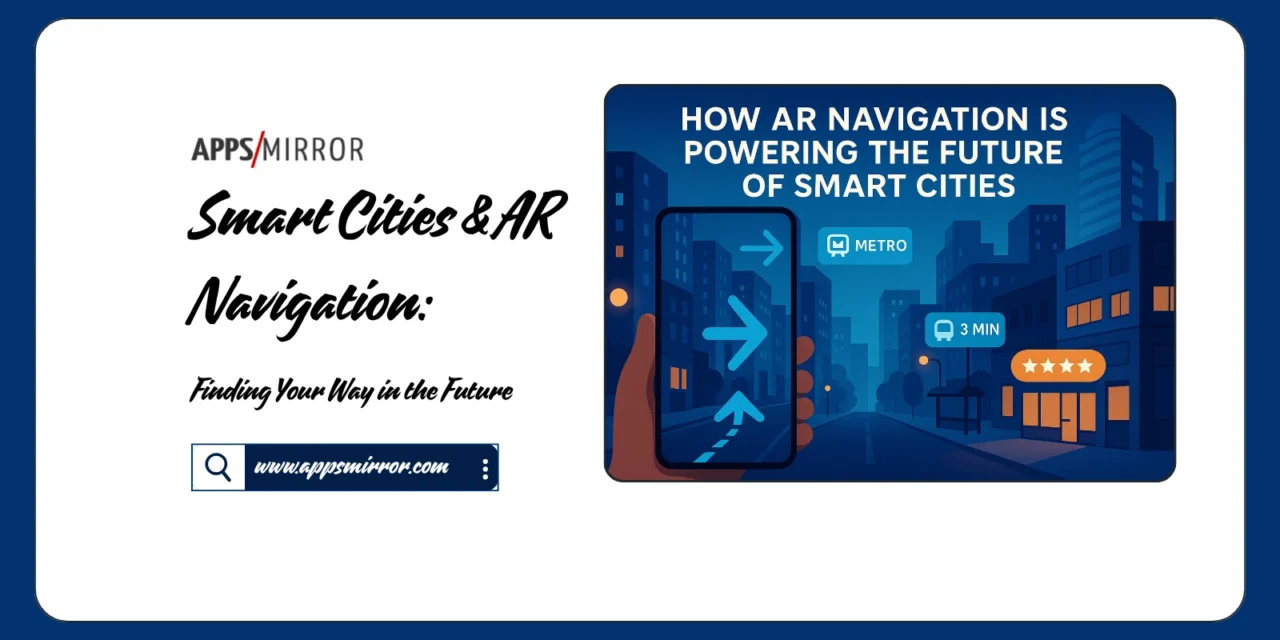
Cities That Think With You
Urban life is complicated—traffic jams, confusing public transport systems, endless searches for the right café or office building. Smart cities, powered by sensors, data analytics, and automation, are designed to make city living smoother. Now add Augmented Reality (AR) to the mix, and the result is navigation that doesn’t just tell you where to go—it shows you, directly on the world around you.
Imagine pointing your phone at a street and instantly seeing arrows guiding you to the subway, bus arrival times floating above stops, or reviews of restaurants glowing over their entrances. Smart cities combined with AR create an environment where information lives in the physical world, not hidden in apps.
AR as the City Guide
Traditional maps require switching between a flat screen and the real environment. AR eliminates this disconnect by overlaying directions and information onto the actual streets and buildings. For pedestrians, this means less confusion and fewer wrong turns. For drivers, AR dashboards could project lane guidance directly onto windshields, reducing accidents.
Tourism is another area set to benefit. Instead of flipping through guidebooks, visitors could walk through cities with AR layers showing historical facts, translations, and event recommendations. It turns urban exploration into an interactive experience.
Transportation Gets Smarter
Public transportation is at the heart of smart cities, and AR can make it more user-friendly. Bus shelters could display live arrival times via AR apps. Train passengers could see seat availability projected over carriages before boarding. Navigation through complex stations—like airports or metro hubs—becomes seamless when arrows and signs are overlaid directly onto the real environment.
For cyclists and walkers, AR can map out eco-friendly routes, highlighting bike lanes or shaded paths that promote healthier and greener lifestyles.
Who’s Building This Future
Tech giants are heavily invested in AR navigation. Google Maps already has AR walking directions in several cities, projecting arrows and street names onto live camera views. Apple is working on AR glasses that may redefine navigation altogether. Meanwhile, startups are focusing on AR for specific use cases—like indoor navigation for malls, hospitals, or airports.
Smart city initiatives in places like Singapore, Dubai, and Helsinki are experimenting with AR layers that integrate with city-wide data systems. These early adopters are setting the stage for broader deployment worldwide.
Advantages and Challenges
Merits:
- Makes urban navigation intuitive and accessible.
- Reduces travel stress and accidents through clearer directions.
- Boosts tourism with immersive, real-time experiences.
- Supports sustainable living by highlighting eco-friendly choices.
Demerits:
- Requires advanced devices and strong internet connectivity.
- Raises privacy concerns if AR apps collect location and personal data.
- Implementation costs may be too high for smaller cities.
- Risk of information overload if not designed carefully.
Balancing innovation with accessibility and privacy will determine how successfully AR integrates into smart cities.
Everyday Life With AR Navigation
In the near future, AR could become part of daily routines. Students might use AR to find classrooms in sprawling campuses. Shoppers could navigate malls with AR maps showing store locations and discounts. Emergency responders could see real-time data overlays guiding them to incidents faster.
For people with disabilities, AR navigation could provide accessibility features like audio cues, object recognition, or enhanced text visibility, ensuring cities become more inclusive.
The Road Ahead
As hardware like AR glasses becomes mainstream, AR navigation will move from phones to wearables. Instead of looking down at screens, people will see directions seamlessly integrated into their line of sight. Combined with AI, these systems will learn personal habits and suggest routes tailored to individual preferences—whether fastest, safest, or most scenic.
Ultimately, AR will help transform smart cities into living, breathing ecosystems where technology and daily life blend seamlessly.
Technology for Good
At its core, AR navigation in smart cities isn’t about flashy gimmicks—it’s about creating environments where people feel empowered, safe, and connected. By making cities easier to navigate, AR reduces stress, promotes sustainability, and makes urban life more inclusive.
When designed responsibly, AR in smart cities can ensure that the benefits of technology are felt by everyone, not just the tech-savvy. It’s not just about finding your way—it’s about building cities that find ways to serve their citizens better.